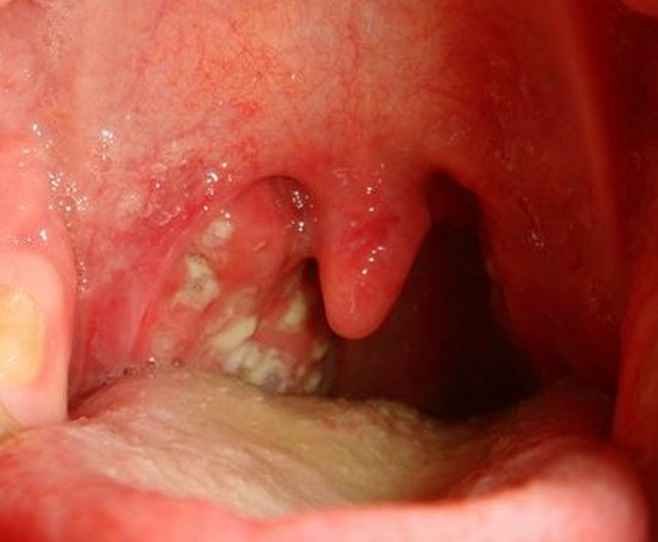
Structure of Tonsils
- The tonsils (also known as palatine tonsils) are a pair of lymphoid tissue mass located in the tonsillar fossa which is present on the lateral wall of the oropharynx.
- The tonsillar mass extends upwards to the soft palate and downwards to the dorsum (lower surface) of the tongue.
- The medial surface which is the freely exposed surface of the tonsils contains pits which give it a pitted appearance. These pits lead to highly branched crypts which extend throughout the thickness of the tonsil.
- The lateral surface of the tonsils is covered by a layer of fibrous tissue known as tonsillar hemi capsule. The tonsils parenchyma consist of populations of lymphoid follicles. The blood supply of the tonsils is from branches of the external carotid artery – mainly by the tonsillar branch of the facial artery, and the veins drain into pharyngeal plexus.
- The tonsils are innervated by tonsillar branches of maxillary and glossopharyngeal nerves.
What are those tiny white spots on your tonsils?
The tonsils are an important structure of the lymphoid tissue. Tonsils are a major site of B lymphocyte proliferation including cells which predominantly produce IgG and IgA antibodies. Tonsils act as reservoirs of B and T lymphocytes. They act as the first line of defence in the immune system against antigens introduced to the body by respiration or ingestion.
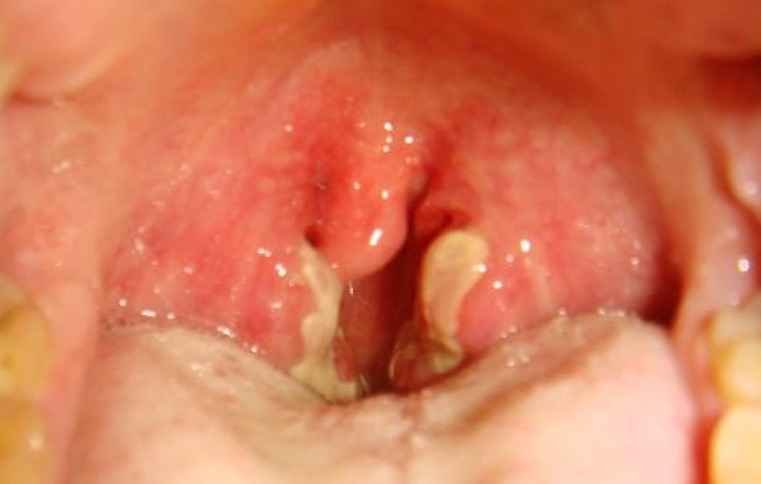
 Picture of white spots on tonsils
Picture of white spots on tonsils
Symptoms of White Spots on Tonsils
Whitish discolouration of the tonsils can be present as streaks or spots or patches and it may be accompanied by other symptoms such as:
- Whitish discolouration of the whole mouth in addition to tonsils
- Upper respiratory symptoms such as cough, sneezing, blocked nose
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Body aches (arthralgia and myalgia)
- Headache
- Lymphadenopathy
- Dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing)
- Odynophagia (painful swallowing)
- Respiratory difficulty
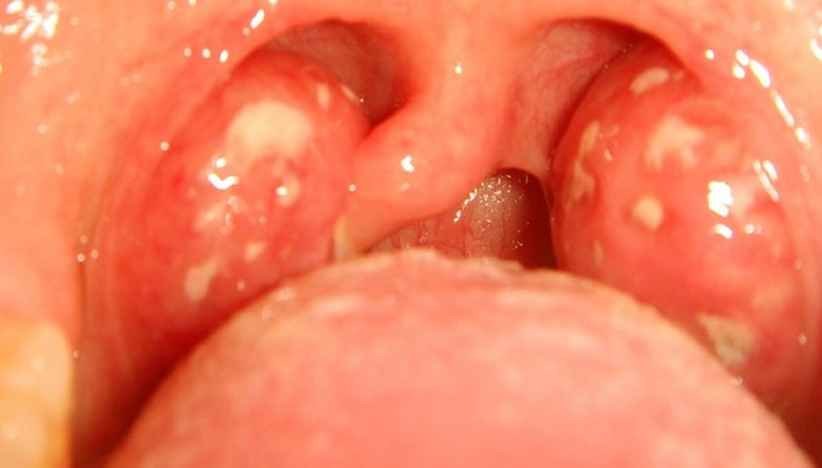
Picture of white spots/dots on tonsils
What Causes White Spots on Tonsils?
Infections are the commonest cause for white spots on tonsils. It can be bacterial, viral or fungal in origin but viral infections are the most common. Few of the common infections are as follows:
Strep throat
It is caused by group-A beta-hemolytic Streptococcus pyogenes bacterial species. This streptococcal pharyngitis is common among infants and children. It is a contagious infection as it can spread via droplets while sneezing and coughing. The tonsils appear to have whitish streaks and spots. Fever, sore throat, headache, body ache and other upper respiratory symptoms also can be present. It can be a recurrent infection in many people.
Tonsillitis
It is the inflammation and infection of the tonsils. It can be due to any bacterial or viral cause. Whitish pus is produced in the tonsils due to the infection. Other upper respiratory symptoms with headache and fever can accompany.
Infectious mononucleosis
It is also known as glandular fever which affects the adolescents and young adults. It is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus which spreads through saliva and aerosol. Due to this infection whitish pus is produced in the tonsils. Fever, headache, malaise, sore throat, palatal petechiae, transient macular rash, cervical lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly are other predominant symptoms.
Oral thrush
It is caused by the opportunistic fungus known as Candida albicans. It is common among:
immune deficient people such as transplant patients and neonates, some medical conditions such as uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, HIV infection and pregnancy,
patients who are on corticosteroids and antibiotics for a long period.
In addition to tonsils, white patches can be seen on the palate, inner surface of cheeks, gums and on tongue. Sometimes these white plaques can be painful and may bleed.
Other causes apart from infections are as follows:
Tonsilloliths
Also known as tonsil stones which are small calcium precipitates due to accumulation of mucus, saliva and food particles on the crypts of the pitted medial surface. Bacteria and fungi grow on these accumulations and produce a distinct bad odor. People with poor oral hygiene and chronic tonsillitis are at risk of developing tonsil stones.
Oral cancer
It is a less common cause. Chronic tobacco smokers, alcoholics and people with family history of oral cancers are at high risk of having oral cancer. Non healing ulcers, unexplained bleeding from mouth and hoarseness of voice are few of the other accompanying symptoms.
Treatment
The medical treatment begins with a detailed history and proper clinical examination. The history includes onset and progression of the symptoms, past medical and surgical history, family history and social history. The clinical examination includes general examination, examination of the mouth and throat, checking for lymphadenopathy throughout the body and relevant system examination according to other symptoms.
Investigations include a throat culture and imaging studies. A swab is taken over the white spots of the tonsils and used to culture to diagnose the microorganism responsible for the infection. Throat cultures are very useful as it is clinically difficult to distinguish viral and bacterial origin of the tonsillitis. For example the surface exudates obtained from infectious mononucleosis appear to be more membranous than the bacterial tonsillitis. X ray or CT scans of the neck are necessary if the infection is spread to the internal structures of the neck beyond the fascia. Blood investigations will be helpful in coming to specific diagnosis, e.g. such as in Epstein–Barr infection in infectious mononucleosis.
The medical management depends on the cause and severity of the condition. But in general the medical management can be divided into two categories as supportive treatment and specific treatment.
Supportive measures are common irrespective of the cause. Supportive measures are taken to ensure the hydration and nutrition of the patient as most of the times the patient suffers from pain and difficulty in swallowing. Supportive measures are also taken to control the headache, body aches and fever. Hospital admission may be required in children to administer intravenous fluids and analgesics if they are unable to swallow.
Specific treatment depends on the cause of the condition.
- Strep throat – Antibiotics are prescribed as specific treatment. Penicillin is the commonly used antibiotic. But erythromycin is used if the patient has penicillin allergy. Ten days of antibiotic treatment is required to eradicate the organism from the body and to protect the patient from rheumatic fever. Amoxicillin is recommended to avoid as it can cause a widespread maculopapular rash if the tonsil condition is due to infectious mononucleosis. In addition to the antibiotics, some home remedies such as gargling the throat with warm salt water will help to improve the symptoms.
- Infectious mononucleosis – specific treatment is not necessary in majority of the cases as the recovery is rapid. But a course of corticosteroids is recommended if there is any respiratory difficulty due to obstruction by enlarged tonsils or if there are any neurological involvement such as meningitis and Guillain-Barre syndrome or when there is marked thrombocytopenia (abnormally low platelet count) and haemolysis. Adequate bed rest and fluids are crucial for quick recovery.
- Oral thrush – treatment method is decided according to the age and health condition of the patient. In healthy adults and children, topical antifungal medication will be adequate. If topical antifungals are not responding, oral antifungals are recommended. In immune depressed adults a course of oral antifungal are recommended. In infants who are breastfed by mothers a mild antifungal is given for the baby and a topical antifungal cream is given for the mother to apply on her breasts. The underlying cause should be addressed properly and treated well in addition to the specific antifungal treatment. Maintaining a good oral hygiene will help in preventing oral thrush.
- Tonsil stones – the treatment can range from simple home remedies to tonsillectomy. Home remedies include gargling with warm salt water as it can reduce the irritation and help to minimize the odour. Medical management includes antibiotics and antifungal as they help to reduce the growth of bacteria and fungi on the precipitates. Further treatments options comprise of elimination of the crypts on the tonsils where the deposits accumulate. It can be done either by laser tonsil cryptolysis or by coblation cryptolysis. Surgical procedure of tonsillectomy is considered if medical management is not responding.
- Oral cancer – specific medical and surgical treatment should be considered.
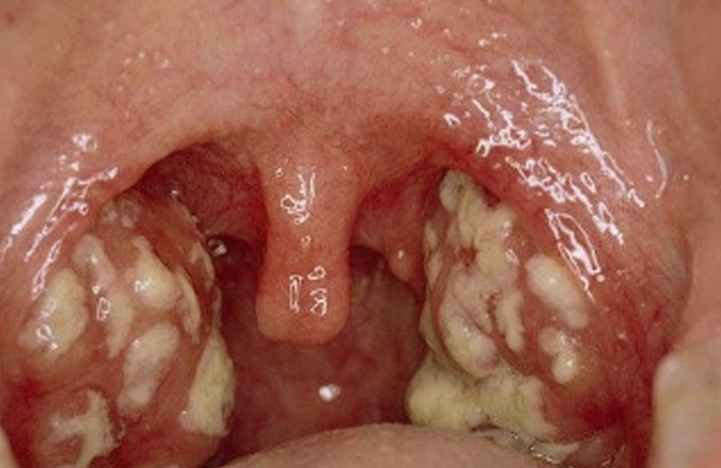
Pictures of White spots on tonsils
Collection of pictures, photos of white spots, dots, patches on tonsils: